
M&A Report: Boeing’s $4.7 Billion Acquisition of Spirit AeroSystems
1. Overview of the Acquirer: The Boeing Company
Boeing Company (NYSE: BA) is a leading global aerospace and defense corporation headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. Established in 1916, Boeing operates through multiple segments, including Commercial Airplanes, Defense, Space & Security, and Global Services. The company is renowned for its innovation in aviation technology and plays a pivotal role in the global aerospace industry, serving customers in over 150 countries. As of mid-2024, Boeing has a market capitalization exceeding $130 billion and is recognized as the largest exporter in the United States, contributing significantly to the economy through its extensive supply chain and workforce.
2. Overview of the Target: Spirit AeroSystems
Spirit AeroSystems (NYSE: SPR) is one of the world’s largest manufacturers of aerostructures for commercial and defense aircraft. Founded in 2005 and headquartered in Wichita, Kansas, Spirit specializes in the design and production of critical components such as fuselages, wings, and nacelles. The company operates facilities across the U.S., U.K., France, Malaysia, and Morocco, and has established itself as a key supplier for major aerospace manufacturers, including Boeing and Airbus. Despite its capabilities, Spirit has faced challenges as an independent entity, leading to this strategic acquisition by Boeing.
3. Deal Terms
Boeing has entered into a definitive agreement to acquire Spirit AeroSystems for approximately $4.7 billion in an all-stock transaction. Under the agreement, Spirit shareholders will receive $37.25 per share of Boeing common stock, representing a 30% premium over Spirit’s closing stock price of $28.60 on February 29, 2024. The total enterprise value of the deal, including Spirit’s net debt, is approximately $8.3 billion. The transaction is expected to close in mid-2025, pending regulatory approvals and customary closing conditions.
4. Key Financial Impacts
- Market Expansion: The acquisition is anticipated to enhance Boeing’s production capabilities and market presence, particularly in the aerostructures segment.
- Cost Synergies: Boeing expects to achieve significant cost synergies through the integration of Spirit’s operations, although specific figures have not been disclosed.
- Operational Efficiency: The merger is projected to improve operational efficiencies and align production systems, which may lead to enhanced safety and quality management.
- Earnings Accretion: The deal is expected to be accretive to Boeing’s earnings per share (EPS) in the second full year post-closing.
5. Deal Analysis
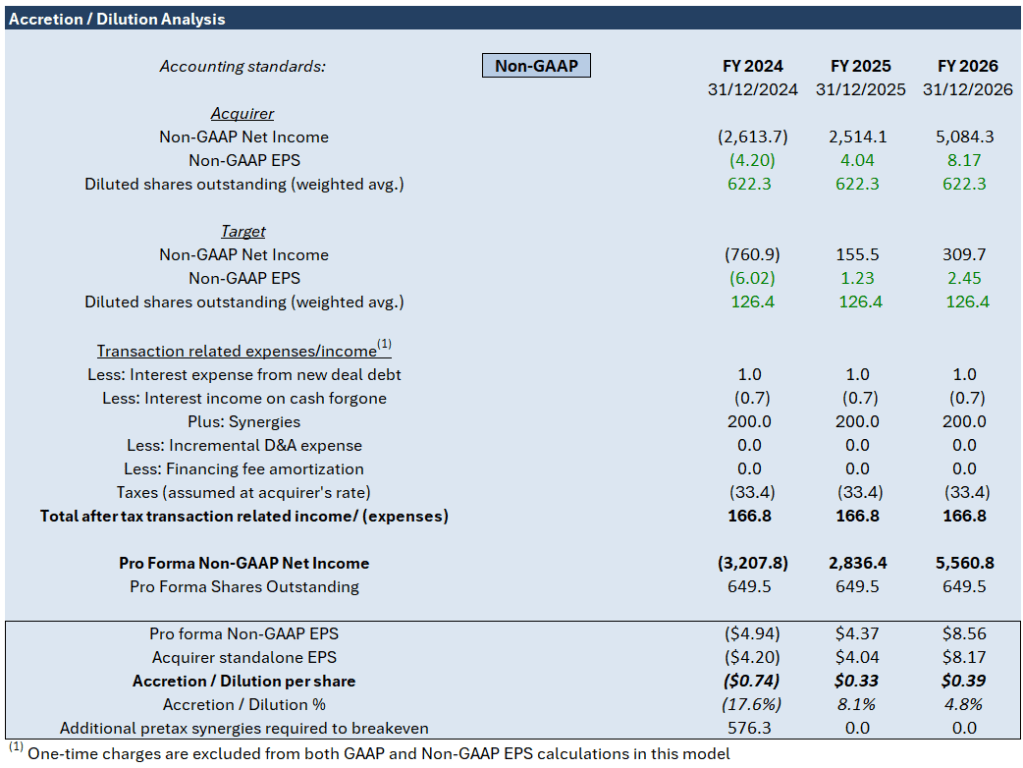
Key Impacts:
Non-GAAP EPS Impact:
- FY 2024: Dilution of -$0.74 per share (-17.6%)
- FY 2025: Accretion of $0.33 per share (8.1%)
- FY 2026: Accretion of $0.39 per share (4.8%)
Synergies: The model anticipates annual synergies of $200 million, contributing positively to the post-transaction financial outlook.
Transaction Expenses:
- Interest expense related to new deal debt: Minimal at $1.0 million annually.
- Interest income on cash forgone: Negligible at -$0.7 million annually.
- Incremental D&A expense, financing fee amortization, and other adjustments: Not applicable or zero in this scenario.
- Total after-tax transaction-related income: Estimated at $166.8 million annually.
Summary:
The analysis of the merger shows a negative impact on EPS for FY 2024, with a dilution of -$0.74 per share (-17.6%). However, the EPS turns accretive in subsequent years, with $0.33 per share (8.1%) in FY 2025 and $0.39 per share (4.8%) in FY 2026, indicating that the transaction becomes beneficial after the initial year. The expected synergies of $200 million per year substantially bolster the financial performance post-transaction, underscoring the strategic rationale behind the merger despite the initial dilution.
6. Opportunities for the Acquisition
- Strategic Alignment: The acquisition aligns with Boeing’s strategy to consolidate its supply chain and enhance its manufacturing capabilities by bringing back a critical supplier.
- Innovation and Integration: By combining Spirit’s manufacturing expertise with Boeing’s technological advancements, the acquisition is expected to drive innovation and improve product quality.
- Strengthened Market Position: The merger will solidify Boeing’s position as a leader in the aerospace sector, particularly in the production of commercial aircraft components.
7. Risks of the Acquisition
- Regulatory Approvals: The transaction is subject to regulatory scrutiny, which could delay or complicate the closing process.
- Integration Challenges: Merging two large organizations with distinct operational focuses may present challenges, particularly in aligning business processes and corporate cultures.
- Divestiture of Assets: Concurrently with the acquisition, Spirit has entered into a binding term sheet with Airbus to divest certain assets, which may impact the overall integration strategy.
Conclusion
Boeing’s acquisition of Spirit AeroSystems represents a strategic move to enhance its operational capabilities and market presence in the aerospace industry. The deal offers potential for significant synergies, operational efficiencies, and improved product quality. However, the success of the acquisition will depend on effective integration, regulatory approvals, and the management of potential risks associated with merging the two organizations.